您现在的位置是: 首页 > 教育分析 教育分析
英语高考常用语法,高考常考的英语语法
tamoadmin 2024-05-28 人已围观
简介1.高中英语语法总结2.高考英语语法复习系列讲座-名词性从句3.高中英语语法详细讲解4.高考英语语法: 省略介词的七种常见情形15.高考英语语法:高中英语语法-主谓一致6.高考英语语法:高中英语语法-实用英语五十句7.高考英语语法填空必背知识 高中英语语法固定搭配用法介绍 1.It’sthe first time that……….(从句中用现在完成时)
1.高中英语语法总结
2.高考英语语法复习系列讲座-名词性从句
3.高中英语语法详细讲解
4.高考英语语法: 省略介词的七种常见情形1
5.高考英语语法:高中英语语法-主谓一致
6.高考英语语法:高中英语语法-实用英语五十句
7.高考英语语法填空必背知识
高中英语语法固定搭配用法介绍
1.It’sthe first time that……….(从句中用现在完成时)
It wasfor the first time that………(强调句,对状语for the first time进行强调)
It’s(high) time that……..(从句中用过去时或should do)
2.It’sthe same with sb. / So it is with sb.表示某人也如此(用于前句中既有肯定又有否定或两个不同类的谓语动词)
3. …beabout to do / be doing……when…….正要做/正在做……就在那时…….
4.A istwice / three times as +原级+as B A是B的两倍/三倍
A istwice / three times the n. of B. A的…是B的两倍/三倍
A istwice / three times +比较级+than B A比B多两倍/三倍
5.It’s awaste of time / money doing / to do…做……浪费时间/金钱
It’s nouse / good doing……… 做……是没有用的
It’spossible / probable / (un) likely that………. 很可能……
It makesgreat / no sense to do……做某事很有/没意义
6. There’sno use / good doing……. 做……没有用
There’s no sense / point (in) doing…… 做……没有意义
There is no need for sth. / to do……. 没有过必要做……
There is (no) possibility that…………(同位语从句)很可能/没可能……
7.The+比较级……..,the+比较级………越…….., 越…….
注意:前半句为从句,用一般现在时代替将来时;
8.Itseems / appears ( to sb. ) that sb…….在某人看来某人………
= Sb.seems / appears to be / to do / to be doing / to have done……..
It seems / looks as if……….好象/似乎……..
9.It (so)happened that sb. ……..某人碰巧……..
= Sb. happened to be / to do / to be doing /to have done…..
10.It issaid / thought / believed / hoped / supposed …….that sb………
=Sb. issaid to be / to do / to be doing / to have done……….(注意:这种句型里如带动词hope则不能变成简单句,因为无hopesb. to do结构)
12.…….such…….that…….如此…….以致于(引导结果状语从句)
…….such……..as……像……..的这种……(as为关系代词,引导定语从句,在从句里充当主、宾、表)
13. Doyou mind if I do sth.? / Would you mind if I did sth.? 你介意我做……吗?
14. Thechance is that……../ (The )Chances are that……….很可能…….
15.Check/ Make sure / See to it / See that……..(从句中常用一般现在时) 确信/务必……..
16.depend on it that……..取决于
see to it that…….负责/设法做到…….
注意:除了except / but / in等介词可以直接接that从句,其它介词后必须用it做形式宾语;
17.It is/ was +介词短语/ 从句/ 名词/代词等+that………
How /When / Where / Why is / was it that………..?
注意:此句型为强调句,当被强调的为表示人的词时,还可用who连接;强调主语时,从句后的谓语动词应与前面的主语保持一致;注意与定语从句的区别)
18.How isit that……..(这几个句型都表示“怎么会…….?” “怎么发生的?”)
How come+从句?
How does / did sth. come about? ( How did itcome about that…….?)
如:How come you are late again?
19. Thereseems / appears / happens to be / must be / can’t be / is (are, was, were) saidto be / is (are, was, were) thought to be…….
表示 “.似乎有/碰巧有/一定有/不可能有/ 据说有/认为有……..”
介词(如of )there being
want /wish / expect there to be要/希望/期待有……..
adj. /adv. enough for there to be…….足够…….会有…….
注意:there being / there to be为therebe的非谓语形式;It is said / thought that there is / are……=Thereis / was / are / were said (thought) to be……. 如:
Eg: Ihave never dream of there being such a good chance for me.
It won’t be cold enough for there to be afrost tonight.
20. 疑问词+插入语+陈述语序?
Eg: Whodo you think he’ll have attend the meeting?
本文就是为大家整理的高中英语语法:固定搭配用法,希望能为大家的学习带来帮助,不断进步,取得优异的成绩。
快速提升英语阅读,需要养成的.十个好习惯
1.不要反复浏览。凡是科技读物,一般只须顺着读一遍即可。如有必要,也要等整篇读完之后,再回过头重复某项内容。避免眼睛不断地来回转动。
2.采用“筛选”式阅读法。有意识地为涉猎专业所需的信息而读。
3.要默读,不要朗读。发声的阅读是快速法的大敌。
4.阅读时,视线应与读物成垂直线,并充分发挥视线的“余光”作用,多览到一些内容。
5.要聚精会神地阅读。必须有“强化”的注意力。
6.提倡有理解地阅读。阅读时,抓住实质性的关键词。读物的内容实质,正是阅读时应弄通的重点。理解,就是探索出读物的思想意义。
7.在阅读中,运用要领的基本,有目的地去记。不必去记无关紧要的词句,却要记住作者意图及内容实质。
8.学会运用多种形式的法,不断提高阅读速度。
9.经常训练自己的阅读,便能巩固已经取得的成果。
10.每天阅读的定额标准——在两份报纸,一本杂志 高考,按自己的专业需要,从中吸取相当于普通图书五十至一百页左右的信息。
;高中英语语法总结
关于 高二英语 语法,英语语法对大家的学习非常重要,大家应该重视英语语法的学习,英语语法知识点比较繁杂,要学好英语语法,大家必须对语法进行整理。下面给大家带来一些关于高中英语语法知识点整理,希望对大家有所帮助。
高中英语语法知识点整理1
不定冠词
不定冠词a,an与one同源,表示微弱的一的概念,但并不强调数目,用来表示不确定的人或事物。
A用在辅音前,而不是辅音字母前;an用在元音前,而不是元音字母前。
a university in Asia
1.表示同类中的任何一个
A cat has nine lives.
2.表示泛指的某人、某物
I know a John Lennon,but not the famous one.
3.表示数量的
He has a daughter.
4. 表示单位数量的每一
I earn 10 dollars an hour.
5.表示相同的
The two birds are of a color.
6. 用于集体名词前
He grows up in a large family.
7. 在某种情况下可用于抽象名词和物质名词前
China has a long history.
高中英语语法知识点整理2
定冠词的用法
1.表示特定的人或物
2.表示地球、宇宙中独一无二的事物
主要指各种天体及世界上比较有影响的物体。The sun,the moon,the earth
3.表示地点、方向、时间、方式等 at the corner 在拐角处
1) 在表示季节的名词前常不用冠词。In spring 在春天
2) 具体某年的某个季节,需用冠词。In the summer of the year2008
3)用于序数词或形容词的最高级前 the first the second
4)用于形容词前使其名词化 the rich the poor
5)用于复数姓氏前,表示―夫妇‖或全家 The Smiths
6)用于乐器名词前 Play the piano
7)用于by+the+计量单位名词 By the pound
1. 用于复数名词前
复数名词泛指某类人或物时,其前通常用零冠词。Students should obey the school rules. 学生应该遵守校规。复数名词若需特指,则要加定冠词。The students are too lazy. 这些学生太懒。
2. 用于不可数名词前
不可数名词表示泛指时,其前通常用零冠词。如:Bread is made from flour. 面包是用面粉做的。
Wood is a poor conductor of sound. 木头是声音的不良导体。不可数名词若需特指,则要加定冠词。
He sawed the wood into three pieces. 他把木头锯成三块。
3.用于专有名词前
在通常情况下,专有名词前要用零冠词。如:
Mr Smith is our English teaches us English. 史密斯先生教我们英语。在特殊情况下,若专有名词需要特指,也可加定冠词。如:The Smith you‘re looking for no longer lives here.
4. 用于抽象化的可数名词前
有些可数名词抽象化后表示表示的活动,其前通常零冠词。Jim has gone to bed. 吉姆已上床睡觉了。
She goes to church every Sunday. 她每周星期天都去做礼拜。
这类主要涉及bed, church, class, college, school, university, work, hospital, prison, market, sea, town等。另外,这类名词前用不用冠词有时与英美英语的表达习惯有关。如:―住院‖在英国英语中通常说成 in hospital,而在美国英语中则通常说成in the hospital;类似的还有go to university (英)上大学 / go to the university (美)上大学;at table (英)在吃饭 / at the table (美)在吃饭。
5. 用于职务及头衔前
当表示职务及头衔的名词用作表语、补足语及同位语时,其前通常用零冠词。如:Wilson became President of the U. S. A. 威尔逊当了美国总统。He will be made captain of the football team. 他将被选为 足球 队队长。
6. 在表示学科、语言、三餐、月份、季节、节假日、星期等名词前,通常用零冠词。
We are all interested in physics. 我们大家都对物理感兴趣。
7. 用于某些固定结构中
go to sea 去当水手 at home 在家 at night 在晚上 at least 至少
at most 至多 at first 首先 at last 最后 in bed 在床上
on foot 步行 face to face 面对面
高中英语语法知识点整理3
代词
高考中对代词的考查主要集中在人称代词(主要是其中的it)、关系代词、指示代词和不定代词上。
一、 it的用法 1.作人称代词
John likes playing Ping pong./ He always does it in the afternoon.(指代上下文提到的事物); /It's time we went home. / How far is it from here to your home ? / It is getting warmer and warmer./ It's very quiet at the moment.(可指时间、天气、环境等) 2.引导词
A.作形式主语,代替由不定式、动名词或从句表示的真正主语。
It's important for us to learn a second language./ It's no use talking to him./ It's known to all that the earth goes round the sun.
B.作形式宾语,代替由不定式、动名词或从句表示的真正宾语。
We feel it our duty to help others./ He made it clear that he would leave the city. C.强调结构:It is (was) +被强调部分+that (或who)…
注意:在强调结构中,如被强调部分为时间状语或地点状语,其后的连接词也绝不能为when 或where,而应用that 。在复习中,一定要注意句式的不同。It was in Shanghai that I bought the guitar.(that引起强调句) It was Shanghai where I bought the guitar.(where引起定从)
It was twelve o'clock when we arrived there.(when引起时间状语从句) It was at twelve o'clock that we arrived there.(that 引起强调句)
3. it,one,that 的区别:作为代词,这三个词的对比使用是高考的 热点 之一。—Why don't we take a little break? —Didn't we just have __________? A.it B.that C.one D.this
The Parkers bought a new house but _________will need a lot of work before they can move in. A.they B.it C.one D.which
one 用以指代同类事物中的任一,that 特指性强,指代可数与不可数词,而it指代上文提过的同一事物。
高中英语语法知识点整理4
关系代词
who,whose,whom,which,that,as
1)which可以引导非限定性定语从句,代表前面整个 句子 的内容,并且在从句中做主语 2)that的用法 1)不用that的情况
a) 在引导非限定性定语从句时。b) 介词后不能用。
We depend on the land from which we get our food. We depend on the land that/which we get our food from.
2) 只能用that作为定语从句的关系代词的情况 a) 在there be 句型中,只用that,不用which。
b) 在不定代词,如:anything, nothing, the one, all, much, few, any, little等作先行词时,只用that,不用which。
c) 先行词有the only, the very修饰时,只用that。d) 先行词为序数词、数词、形容词最高级时,只用that。. e) 先行词既有人,又有物时。
举例:
All that is needed is a supply of oil. 所需的只是供油问题。
Finally, the thief handed everything that he had stolen to the police. 那贼最终把偷的全部东西交给了警察。
3) as的用法
AS作关系代词,用来引导定语从句:限制性定语从句和限非制性定语从句 一、AS引导限制性定语从句
AS引导限制性定语从句时,通常和such, the same, as(so)等连用,构成such...as/such as, the same...as/the same as, as(so)...as等结构,在从句中可作主语,宾语和表语。
1.such...as/such as意为―...的那种...,像那样的‖,such...as/such as引导限制性定语从句时,既可指人,也可指物。such用于名词之前时,具有形容词性质;such单独使用(即后面不接名词)时,具有代词性质。
Don‘t trust such men as praise you to your face.(as作主语) 不要相信那种当面吹捧你的人。
You should read only such books as you can understand without much difficulty.(as作宾语) 你应当只读那些你读起来不太难懂的书。
Associate with such as will improve your manners.(as作主语) 要和能改善你的言行的那种人结交。
2.the same...as/the same as意为―与...同样的‖,和such一样,the same既有形容词作用,又有代词性质。
We have arrived at the same conclusion as they have.(as作宾语) 我们已得出和他们同样的结论。
比较:the same...as和the same...that不同,前者是―同那一个相似‖,后者是―正是那一个‖。如:
This is the same watch as I lost. 这同我丢的那块表一样。
This is the same watch that I lost? 这正是我丢的那块表。
3.as(so)...as意为―和...一样‖,后接由many, much等修饰的名词或由形容词修饰的单数名词,注意其语序为as(so)+adj.+a+n+as,如:It‘s as pleasant a film as I have ever seen. 这是一部和我以往看的同样好的**。
As many soldiers as marched were killed. 很多游行的战士都被杀了。
注意:such ...as与such...that ,so...as与 so...that的区别:that是连词,引出结果状语从句,在从句部分不作成分;as是关系代词,引出定语从句,在从句中可作主语,宾语和表语。比较:He is such a nice boy that everyone likes him. He is such a nice boy as everyone likes.
It is so difficult a problem that nobody can work it out. It is so difficult a problem as nobody can workout
高中英语语法知识点整理相关 文章 :
★ 高中英语语法考点总结
★ 高中英语语法知识点
★ 高考英语语法与知识点整理
★ 高考英语语法与知识点总结归纳
★ 高中英语语法总结
★ 高中必备英语知识点归纳
★ 英语高一必修一语法知识点汇总
★ 高中英语知识归纳笔记
★ 人教版高中英语必修一语法知识点总结
高考英语语法复习系列讲座-名词性从句
高中英语语法总结
定语从句 :限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句
名词性从句:主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句
时态:现在完成时 过去完成时 将来完成时 现在完成进行时 过去完成进行时 将来完成进行时
状语从句
非谓语动词的用法
虚拟语气的运用
推荐你个好东东,魏训刚的《高考语法完全突破》视讯教程,非常好用。有配套练习和记忆大纲,三件一套,又叫中学语法三剑客,现在很热,可以搜来看看。
定语从句 ,状语从句,表语从句, 名词性从句(主语从句 宾语从句 同位语从句) 倒装 省略 反意疑问句 动词短语 冠词
满意请采纳,谢谢
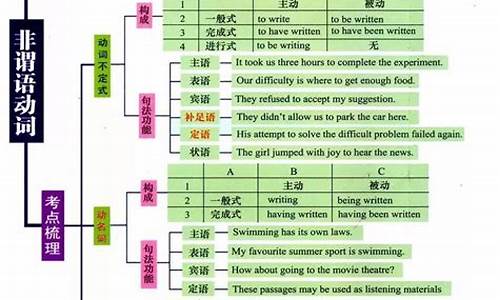
分词(participle)
现在分词一般式 否定式 完成式 被动式
Doing Not doing Having done Being done
Not having done Having been done
Not being done
现在分词,过去分词
现在分词表示被动,表进行;及物动词的过去分词表被动,完成。
Boiling water 正在沸腾的水 boiled water 已经开过的水
The rising sun 正在升起的太阳 the risen sun 升起了的太阳
A developing country 发展中国家 a developed country 发达国家
*现在分词和过去分词都可以在句中作表语,定语,状语和宾语补足语。
作表语
。现在分词作表语一般表示主语的特征和句中主语是主谓关系,主语一般是物,有时也可以是人。
。过去分词做表语一般表示主语所处的状态和句中主语是逻辑的动宾关系,主语一般是人,也可以是物。
(1) the film is moving we are moved
disappoint /surprise /move /frighten /inspire /interest
The boy is disappointing and his father is disappointed.
He tried be calm, but his voice sounded a bit surprised.
be covered /lined with
The door remained locked They remained listening.
2.做定语:
有些词的过去分词有两种 learned /learned burned /burnt lighted/light
一般规则变化的做定语,不规则变化的不做定语
*单独的一个分词做定语通常放在被修饰词的前边,分词短语做定语放在被修饰词的后边,相当于一个定语从句。
1( 使动词的用法
*a girl named Mary came to see me .
*a girl calling herself Mary came to see me .
a moved girl = a girl who was moved a moving film =a film which is moving
a surprised look /expression on his face
2) I read the book written (which was written) by lu xun
Tell the children playing the guitar not to make so much noise.
The building being built is our teaching building.
He lives in a room facing the south.
注:有些词只能用定语从句表达而不能用过去分词的形式。
The boy who came to see me is my brother.
There were aidents that always happened.
3) 现在分词短语和过去分词短语都可以做非限制性定语,相当于一个非限制性定语从句 . The book, written in 1980, tells of struggle.
2.作状语: 时间状语,原因状语,条件状语,伴随状语。
He went into the lab, following other students.
The teacher went into the lab, followed by a group of students.
Being a young people, he is always ready to help others.= as he is a young people ,…..
Given more time, he would do it even better. =if we were more time ,………..
Being ill, he didn’t go to school. = as he is ill ,he didn’t ……..
Not knowing what to do, went to ask marl.
Not having received her lessons well, she failed in the exam.
Having finished her work, she went home.
Getting up early, you’ll catch the bus. =if you get earlier ,……..
considering 就…而言 考虑到,各方面考虑起来
She seems very bright, considering.
Considering the distance, he arrived quickly.
The hall is still in good condition, considering that it was built almost 1000 years ago.
注:1) Generally speaking, he is a good person.
Judging from his skin, he is an African.
He left home, determined not to set his foot in his home.
但是 to tell the truth ,……. To be honest ………
regarding = about 关于…的问题
He spoke to me regarding his failure .
I must speak to you regarding this matter.
2) 分词做状语,分词的逻辑主语必须与主句的主语一致。
While visiting a city, a guidebook is very useful.
While reading the letter, tears e to her eyes. (错误)
当分词做状语,分词的逻辑主语与主句的主语不一致时, 分词可以在自己的前 面加上自己的逻辑主语,这样后构成的短语叫独立主格结构,一般用逗号与主句分开。
It being Sunday .I don’t have to go to work.
He being a party member, his deeds are expected by all.
Our work having been finished, we went home.
They’re being no buses, we went home.
Weather permitting; we’ll start on Saturday.
Mr. *** ith is shy and doesn’t speak until spoken to.
4. 做宾语补足语。
see , watch , hear , notice , feel , find , get , have , leave , keep +n./+分词
I’m sorry to have kept you waiting for such a long time.
When he woke up , he found himself lying on the ground .
Don’t have the medicine working all the time.
I won’t have you talking to your mother like this .否定表示不允许,不容忍。
* get *** . /sth . doing 使。。重新开始
get the clock going get the car going 跑/ start 启动
It’s not hard to get the children speaking, but it’s hard to s them.
I often hear the song sung in English.
he spoke loudly in order to make himself heard clearly .
I saw the boy beaten by tom.
The teacher found jack seated / sitting in the room.
The boy was last seen playing in the river.
注: dress ---- be dressed seat ------be seated fix ---one’s eye be fixed on
We found her dressed in red today.
The thief was caught stealing
Dressed in red, she went out.
We found him hidden behind the door.
We sat there silent, her eyes fixed on that army camp.
I didn’t hear a single word in his talk referring to your absence from the meeting.
Do you know the man referred to at the meeting?
He walked along the river, his hands folded across his shoulder.
Feel one’s heart beating fast. /his face exposed.
Compared with tom, he is an honest man.
Comparing what he had with tom, he is satisfied.
The Gerund 动名词
—。 构成。
语态/形式 一般式 完成式 复合结构
主动 Doing Having done One’s doing
被动 Being done Having been done
否定形式一律在其前加not
II .用途: 定语,宾语,主语,表语
做主语:动名词做主语,谓语动词用单数。
Smoking does harm to your health.
Tom’s ing made us happy.
Her not ing back made her father angry.
His being punished by the teacher is known to us.
Looking after children is her job.
Seeing is believing (前后对应)眼见为实。
Teaching is learning 教学相长。
My falling ill worried him greatly.
注意下列结构: It is no use / good / useful doing
It is no good quarrelling with them.
It is no use regretting what you have done.
2. 定语
动名词做定语表示用途。(即 ving 做定语有两个意思 1)表动作在进行 2)表用途)
a walking stick / a changing room 更衣室/ a hiding place / an operating table
a collecting tin / a weight machine / building material / drinking water / swimming pool
a washing machine / a sleeping car / a *** oking room / sowing machine 播种机
booking office 售票处 / training class 训练班 /translating machine 翻译机
3.作表语,可以与主语互相转换。
His worst habit is eating too fast.
Our job is playing all kinds of instruments.
Their job is making model planes.
The real problem is getting all the materials ready before the end of the month.
The problem is his son’s having taken the other’s money.
4. 做宾语。
动名词既可以做动词宾语,也可以作介词宾语。
He has finished reading the book.
We could hear the noise of the desk’s being opened. and closed.
He came to attend the concert without being invited.
He suggested the text’s being translated into Chinese.
You should practise listening to English.
She looked forward to receiving her mother’s letter.
注意:1)有些动词或动词短语后面, 必须用动名词做宾语,而不用不定式。
enjoy , finish , mind , risk , avoid , forbid , excuse , practise , imagine , suggest , delay , miss , escape , can’t help , consider ,
be worth doing / be busy doing / give up doing / put off doing / insist on doing
keep / prevent /s from doing feel like doing / prefer doing to doing
be afraid of / be tired of / be fond of / be proud of /sueed in
. the wounded solider escaped being killed in the fighting .
do you mind my *** oking here ?
Don’t be afraid of asking for help.
The boy insisted on being severed with cake.
2)要特别注意以下几个片语
pay attention to / look forward to / devote oneself to / make contribution to
stick to / be /get used to / object to / refer to / get down to / see to ( 处理)
He objected to being treated as a child.
The scientist devoted himself to inventing this new machine.
有些动词跟to do 和doing 均可,但意思不同。
fet to do 忘记做/去做一件事 (没有做)
fet doing 忘记过去做过某事 。
I fet to close the window when I left my office.
Don’t fet to post the letter for me.
I fet meeting you in the street the other day.
remember to do 记住去做某事
remember doing 记得做过某事
please remember to close the window when you leave .
I remember having given the book to you.
regret to do 对现在要发生的事情表示遗憾,抱歉。
Regret doing 对已经发生的事情表示后悔。
I regret to say / to tell you that I can’t go with you.
He regretted having told you about it.
mean to do 打算,想要做,有做某事的意图。
Mean doing 意味着
I mean to go with you.
He didn’t mean to hurt you.
It means finishing in time.
Giving him such books to read means waste his time .
e. try to do 试图于,设法干,尽力于
try doing 试着干
The boy tried to open the door.
He tried driving a bus.
s to do /doing
go on to do / doing
be sure to do 肯定会 ,讲会者肯定
be sure of doing 主语自己会
He is sure to e
I am sure of his ing.
H. like /hate to do
Like hate doing
Nobody likes being laughed at.
4. 注意: need, want require +doing = need, want, require to be done
The room wants cleaning / to be cleaned
The child needs looking after / to be looked after
5. 有些 介词加doing 表示时间
on /upon doing = as soon as
in doing = when /while
On hearing the news, he jumped with joy.
In working in shanghai, he made a lot of friends.
=While working in shanghai, he made a lot of friends.
定语从句 ,状语从句,表语从句, 名词性从句(主语从句 宾语从句 同位语从句) 倒装 省略 反意疑问句 动词短语 冠词
语专家葛传槼先生曾说:“语法是语言的法则。”英语语法是英国语言的实际用法,是通过语法家的调查研究、分析、综合而总结出来的,不是凭空臆造出来的。任何人使用英语,不管他是否学过语法,都必须依照语法。举个极简单的例子说,任何人写或讲“My mother studies English.”这一句,决不可把My改作I或Me,也不可把studies改作study或studys,也不可在English前面加上the。至于他是否知道possessive(所有格),indicative(直陈语言),third person(第三人称),article(冠词)等名称,那是另一问题。<br> 我国的英语学习者大多是十多岁的青少年,或者理解力较强,或者模仿力较强,在没有英语环境的情况下,学习语法,了解所学语言的规则,可以缩短学习过程,掌握英语的规律,尽快提高听、说、读、写、译的能力。<br> 那么,怎样学习语法呢?下面拟从四个方面简要谈一谈:<br> (1)练好基本句型<br> 我国近年来的英语教学实践证明:在初学阶段,采用听说领先、学习基本句型的方法去学习英语语法,是行之有效的。<br> 句型学习是通过听说领先的方法去学习传统语法里最常用的语法专案(把它们变为句型去操练)。句型训练实际上吸取了传统语法与结构语法两派的长处。目前国内的英语广播(电视)教学,在入门阶段,多采用句型教学法。因此学生们或者收听广播(收看电视)进行学习,或者根据所选用的课本提供的句型用替换词进行替换练习。所学的句型应该是由浅入深,由简到繁;讲求熟练掌握,不要贪多冒进。每学一个专案,首先要把单项练习练熟,然后过渡到综合练习,最后则应做到扩大运用。<br> 以定语从句这一项为例,首先要反复进行替换练习。把“I read a novel yesterday.”和“It was extremely Interesting.”这两个单句改为“The novel I read yesterday was extremely interesting.”这就是定语从句的单项练习。再如把“I saw a man this morning.”和“The man is my teacher.”改为“The man I saw this morning is my teacher.”;把“I saw a film last night.”和“The film was very amusing.”改为“The film I saw last night was very amusing.”这种练习虽然是枯燥的,却是重要的基本功,把定语从句练到脱口而出的地步。这是第一步。<br> 第二步是把定语从句放在一定的语言情景中去综合运用,进行一问一答。如:<br> A:Did you enjoy the opera?<br> B:Which opera?<br> A:The one we saw last night,of course.<br> B:Yes,very much.<br> 第三步是扩大运用,也就是把定语从句和以前学过的两三个专案放在一起去操练。<br> A:Do you know who Edgar Snow was?(一般疑问句;宾语从句)<br> B:Yes,he was an American writer who interviewed Chairman Mao in Beijing.(定语从句)<br> A:Oh,now I remember.He was the author who wrote“Red Star Over China”,wasn't he?(定语从句;反意疑问句)<br> B:Exactly.<br> 这种回答不但练了定语从句,而且复习了一般疑问句和反意疑问句,也给名词从句的学习打了“埋伏”。进行句型操练,既需要“滚雪球”(复习已学的专案),也需要“打埋伏”(预先练一下将来要学习的专案)。<br> 在句型学习阶段必须注意:在听、说领先的前提下,写、读要跟上,力求听、说、写、读四会均衡发展。因此,时间上要做出合理的安排。早上通常可安排为朗读时间。如果能每日坚持下去,收效一定很大。<br> (2)结合课文去学<br> 吕叔湘先生说过:“与其多读语法书,不如多读文章。”又说:“词语要嵌在上下文里才有生命,才容易记住,才知道用法。”(引自《中国人学英语》)课文是学习英语的“重要基地”。课文里有语音、词汇专案,也有各类语法专案。它们有机地结合在课文里。课文中出现的语法专案,是有血有肉的,不是干巴巴的。通过课文去学语法,可以学得活,记得牢,这比孤零零地背诵语法条目要有效得多。因此,在句型学习结束后,宜结合课文去学语法,要围绕课文中出现的主要语法专案,循序渐进地学习比较系统的语法知识。
语专家葛传槼先生曾说:“语法是语言的法则。”英语语法是英国语言的实际用法,是通过语法家的调查研究、分析、综合而总结出来的,不是凭空臆造出来的。任何人使用英语,不管他是否学过语法,都必须依照语法。举个极简单的例子说,任何人写或讲“My mother studies English.”这一句,决不可把My改作I或Me,也不可把studies改作study或studys,也不可在English前面加上the。至于他是否知道possessive(所有格),indicative(直陈语言),third person(第三人称),article(冠词)等名称,那是另一问题。
我国的英语学习者大多是十多岁的青少年,或者理解力较强,或者模仿力较强,在没有英语环境的情况下,学习语法,了解所学语言的规则,可以缩短学习过程,掌握英语的规律,尽快提高听、说、读、写、译的能力。
那么,怎样学习语法呢?下面拟从四个方面简要谈一谈:
(1)练好基本句型
我国近年来的英语教学实践证明:在初学阶段,采用听说领先、学习基本句型的方法去学习英语语法,是行之有效的。
句型学习是通过听说领先的方法去学习传统语法里最常用的语法专案(把它们变为句型去操练)。句型训练实际上吸取了传统语法与结构语法两派的长处。目前国内的英语广播(电视)教学,在入门阶段,多采用句型教学法。因此学生们或者收听广播(收看电视)进行学习,或者根据所选用的课本提供的句型用替换词进行替换练习。所学的句型应该是由浅入深,由简到繁;讲求熟练掌握,不要贪多冒进。每学一个专案,首先要把单项练习练熟,然后过渡到综合练习,最后则应做到扩大运用。
以定语从句这一项为例,首先要反复进行替换练习。把“I read a novel yesterday.”和“It was extremely Interesting.”这两个单句改为“The novel I read yesterday was extremely interesting.”这就是定语从句的单项练习。再如把“I saw a man this morning.”和“The man is my teacher.”改为“The man I saw this morning is my teacher.”;把“I saw a film last night.”和“The film was very amusing.”改为“The film I saw last night was very amusing.”这种练习虽然是枯燥的,却是重要的基本功,把定语从句练到脱口而出的地步。这是第一步。
第二步是把定语从句放在一定的语言情景中去综合运用,进行一问一答。如:
A:Did you enjoy the opera?
B:Which opera?
A:The one we saw last night,of course.
B:Yes,very much.
第三步是扩大运用,也就是把定语从句和以前学过的两三个专案放在一起去操练。
A:Do you know who Edgar Snow was?(一般疑问句;宾语从句)
B:Yes,he was an American writer who interviewed Chairman Mao in Beijing.(定语从句)
A:Oh,now I remember.He was the author who wrote“Red Star Over China”,wasn't he?(定语从句;反意疑问句)
B:Exactly.
这种回答不但练了定语从句,而且复习了一般疑问句和反意疑问句,也给名词从句的学习打了“埋伏”。进行句型操练,既需要“滚雪球”(复习已学的专案),也需要“打埋伏”(预先练一下将来要学习的专案)。
在句型学习阶段必须注意:在听、说领先的前提下,写、读要跟上,力求听、说、写、读四会均衡发展。因此,时间上要做出合理的安排。早上通常可安排为朗读时间。如果能每日坚持下去,收效一定很大。
(2)结合课文去学
吕叔湘先生说过:“与其多读语法书,不如多读文章。”又说:“词语要嵌在上下文里才有生命,才容易记住,才知道用法。”(引自《中国人学英语》)课文是学习英语的“重要基地”。课文里有语音、词汇专案,也有各类语法专案。它们有机地结合在课文里。课文中出现的语法专案,是有血有肉的,不是干巴巴的。通过课文去学语法,可以学得活,记得牢,这比孤零零地背诵语法条目要有效得多。因此,在句型学习结束后,宜结合课文去学语法,要围绕课文中出现的主要语法专案,循序渐进地学习比较系统的语法知识。
分词(participle)现在分词一般式 否定式 完成式 被动式 Doing Not doing 百度一下奥风英语的中学语法三剑客就行了
求高中英语语法总结内容太多,给你网址,自己去看,望能采纳~~~~
:baike.baidu./view/328219.htm
高中英语语法总结 ····全去网上搜《高考语法完全突破》视讯教程或是与之配套的记忆大纲吧,直接针对高考,非常全的。
高中英语语法详细讲解
语法复习三:名词性从句
在前面我们已经知道了什么是句子.我们可以这样解释什么叫从句:在一个句子的前面加上一个连接词,这个句子就变成了从句.如果这个从句做了主语,它就是主语从句.其它的以此类推.
注: 1.特殊疑问句本身可以做从句,它不需要加连接词.
2.所有的从句要使用陈述语序. 陈述语序: 句子第一个词永远是主语;第二个词可能是情态动词\助动词等加上动词,或者是动词本身.
名词性从句相当于名词,可分别作主句的主语、表语、宾语和同位语。因此,名词性从句分为主语从句、表语从句、宾语从句和同位从句。
名词性从句,顾名思义,它具有名词性.所以可以作主语,宾语等等.回忆一下句子成分那一章
(一)引导名词性从句的连接词
1、连接代词:who, whose, whom, what, which。有词义,在从句中担任成分,如主语、表语、宾语、或定语等。
2、连接副词:when, where, why, how。有词义,在从句中担任成分,作状语。
3、连接词:that, whether, if, as if, that
(二)主语从句
1、主语从句在复合句作主语。
Who will go is not important.
2、用it作形式主语,主语从句放在句末。
It doesn’t matter so much whether you will come or not.
3、that引导主语从句时放在句首时,不能省略。
That he suddenly fell ill last week made us surprised.
实用例句:
Is it true that he will be punished seriously by the headmaster?
Does it make any difference who bought these gifts?
How strange it is that these children are so quiet!
注意: 表示是否,只能使用whether.
(三)表语从句
1、表语从句在复合句中作表语,位于系动词之后。
The question was who could go there.
2、引导表语从句的连接词that有时可省去。
My idea is (that) we can get more comrades to help in the work.
注意: 表示是否,只能使用whether.
(四)宾语从句
1、宾语从句在复合句中作宾语。引导宾语从句的连词that一般可省略。
I hope (that) everything is all right.
2、介词之后的宾语从句,不可用which或if连接,要分别用what或 whether。
I’m interested in whether you’ve finished the work..
I’m interested in what you’ve said.
3、whether与if都可以引导宾语从句,常可互换。但下面情况不能互换。
if和whether区别
①宾语从句是否定句时,只用if,不用whether。
e.g. I wonder if it doesn’t rain.
②用if 会引起误解,就要用whether。
e.g. Please let me know whether you want to go.(此句如果把whether改成if,
容易当成条件句理解)
③宾语从句中的whether 与or not直接连用,就不能换成if;不直接连用,可换。
e.g. I don’t know whether or not the report is true.
I don’t know whether/ if the report is true or not.
④介词后的宾语从句要用whether引导。whether 可与不定式连用。whether也可引导主语从句、表语从句、同位语从句,还可引导让步状语从句,以上均不能换成if。但引导条件从句时,只能用if,而不能用whether。
It depends on whether we have enough time.
They don’t know whether to go there.
Please come to see me if you have time. 状语从句
实用例句: 使用it作形式宾语
I thought it impossible that he could finish this job in just two hours.
He left it to my judgment whether we should continue this project.
注意: 形式主语和形式宾语只有一个替代词: it
(五)同位语从句
同位语从句在句中作某一名词的同位语,一般位于该名词(如:news, fact, idea, suggestion, promise等)之后,说明该名词的具体内容。
I have no idea when he will be back.
The fact that he had not said anything surprised everybody
一、判断下列各句哪句含有名词性从句,并指出是什么从句:
1. China is no longer what it used to be.
2. The truth that the earth turn around the sun is known to all.
3. It was snowing when he arrived at the station.
4. How he persuaded the manager to change the plan is interesting to us all.
5. The news that they had won the game soon spread over the whole school.
6. The news that you told me yesterday was really disappointing.
7. That is where Lu Xun used to live.
8. He spoke as if he understood what he was talking about.
9. Do you remember the teacher who taught us English at middle school?
10. I wonder why she refused my invitation.
参考答案: 1、表语从句;2、同位语从句;3、不是;4、主语从句;5、同位语从句;6、不是;7、表语从句;8、宾语从句;9、不是;10、宾语从句
二、用适当的连词填空:
1. I can’t decide ____________ dictionary I should buy.
2. That’s ____________ he refused my invitation.
3. I am very interested in ____________ he has improved his pronunciation
in such a short time.
4. ____________ we need is more time.
5. The fact ____________ she had not said anything at the meeting
surprised everybody.
6. ____________ and ____________ they will meet has not been decided yet.
7. Please tell me ____________ you are waiting for.
8. Is that ____________ you are looking for?
9. Would you please tell me ____________ the nearest post office is?
10. I don’t know ____________ he will agree to the plan or not.
参考答案: 1. which; 2. why; 3. how; 4. What; 5. that; 6. when, where; 7. who(m); 8. what; 9. where; 10. whether
三、选择填空:
1. Do you see _____ I mean?
A. that B./ C. how D. what
key: D 宾语从句 that引导宾语从句无词义,也不作成分.mean是及物动词,必须有宾语.所以不选A; how是副词,也不能作mean的宾语.what I mean, what I did, what I said,等是一个非常重要的名词结构.
2. Tell me_____ is on your mind.
A. that B. what C. which D. why
key: B what is on your mind 是what名词结构.句意:告诉我你的心事.
3. We must stick to _____ we have agreed on.
A. what B. that C. / D. how
key: A
4. Let me see _____.
A. that can I repair the radio B. whether I can repair the radio
C. I can repair the radio D. whether can I repair the radio
key: B 从句使用陈述语序 注意选项C可以看成是省略了that的宾语从句,在语法上来讲它是正确的,但语义不通.
5. Keep in mind _____.
A. that the teacher said B. what did the teacher say
C. that did the teacher say D. what the teacher said
key: D what名词结构作keep宾语.
6. Could you advise me _____?
A. which book should I read first B. what book should I read first
C. that book I should read first D. which book I should read first
key: D
7. He was criticized for _____.
A. he had done it B. what he had done
C. what had he done D. that he had done it
key: B
8. Would you kindly tell me _____?
A. how can I get to the Beijing Railway Station
B. how I can get to the Beijing Railway Station
C. where can I get to the Beijing Railway Station
D. whether can I get to the Beijing Railway Station
key: B
9. Mrs. Smith was very much impressed by _____.
A. what had she seen in China B. that she had seen in China
C. what she had seen in China D. which had she seen in China
key: C
10. We took it for granted ___
A. that they were not coming B. that were they not coming
C. they were coming not D. were they not coining
key: A
11. I really don't know _____
A. I should do next B. what should I do next
C. what I should do next D. how I should do next
key: C
12. I'm afraid _____.
A. the little girl will have to be operated on
B. that will the little girl have to operate on
C. the little girl will have to operate on
D. that will the little girl have to be operated on
key: A
13. She walked up to _____ .
A. where did I stand B. where I stood C. I stood there D. where I stood there
key: B where I stood 我站的地方
14. Can you tell me _____?
A. who is that gentleman B. that gentleman is who
C. who that gentleman is D. whom .is that gentleman
key: C 陈述语序
15. We'll give you _____.
A. that do you need B. what do you need
C. whatever you need D. whether do you need
key: C whatever: 1. no matter what 表示让步,副词性 2. anything that ,名词性
如果一个副词性的疑问词加上ever后缀,它只具有副词性.如 whenever=no matter when; however 它是一个很特殊的词: 1.表示转折关系,副词,词义:然而 2.no matter how 无论怎么
16. They want us to know _____ to help us.
A. what can they B. what they can C. how they can D. how can they
key: B what they can (do), what作do的宾语.
17. We must put _____ into practice.
A. what we have learned B. that we have learned
C. that have we learned D. what have we learned
key: A
18. Did she say anything about _____?
A. that the work was to be done B. how was the work to be done
C. that was the work to be done D. how the work was to be done
key: D
19. He was never satisfied with _____.
A. what she had achieved B. had what she achieved
C. she had achieved D. that she achieved
key: A
20. These photographs will show you _____.
A. what does our village look like B. what our village looks like
C. how does our village look like D. how our village looks like
key: B
21. Peter insisted _____ he pay the bill.
A. on that B. what C. that D. on which
key: C insist 后面加that从句要用虚拟的形式: should+v, should可省略
22. They urged _____ the library open during the vacation.
A. when B. where C. why D. that
key: D 同上
23. We wish we could have learned _____ when we were at high school.
A. what you did B. that you had done
C. that what you did D. what did you do
key: A
24.1 will describe to you _____ I saw when there.
A. what B. that C. which D./
key: A
25. From _____ I should say he is a good worker.
A. what 1 know of him B. that I do know of him
C. what do I know of him D. that do I know of him
key: A
26. I will give this dictionary to __ wants to have it.
A. whomever B. anyone C. whoever D. someone
key: C any one who wants to have it
27._____ they will come here hasn't been decided yet.
A. What B. That C . When D. Where
key: C
28. _____ was said here must be kept secret.
A. Who B. The thing C. Whatever D. Where
key: C
29. It is still a question _____ we shall have our sports meet.
A. if B. that C. what D. when
key: D
30. I'm going anyway. _____ she will go is up to her to decide.
A. If or not B. Whether or not C. If D. That
key: B
31. It is strange _____ she have left without saying a word.
A. that B. what C. why D. how
key: A
32. It is very clear _____ our policy is a correct one.
A. what B. that C. why D. where
key: B
33. _____ Mr Zhang said is quite right.
A. That B. When C. What D. Whether
key: C
34. It has been decided _____ he will be sent there.
A. if B. whether C. why D. that
key: D
比较: It hasn't been decided whether he will be sent there.
35. It doesn't matter _____he' s come back or not.
A. if B. whether C. that D. when
key: B
36. It's a great pity _____ we won’t be able to finish the task on time.
A. when B. that C. why D. where
key: B
37. It happened _____ I wasn't there that day.
A. when B. why C. where D. that
key: D it happened that... 碰巧...
38._____ you have done might do harm to other people.
A. What B. That C. Which D. The things
key: A
39. _____ leaves the room last ought to turn oft the lights.
A. Anyone B. The person C. Whoever D. Who
key: C anyone who
比较: who left the room last is being looked into.
40._____ the 2000 Olympic Games won't be held in Beijing is known to all.
A. Whether B. If C. Whenever D. That
key: D
41. _____ fails to see this will make a big mistake.
A. That B. Whoever C. Whether D. Whether or not
key: B anyone who
42. __ we need more equipment is quite obvious.
A. What B. Whether C. That D. Whatever
key: C
43. Has it been announced _____?
A. when are the planes to take off B. that are the planes to take off
C. where are the planes to take off D. when the planes are to take off
key: D
44. That is _____ we all support his idea.
A. what B. why C. where D. when
key: B
45. That’s _____ we should do.
A. that B. what C. how D. why
key: B
46. _____ is troubling me is _____ I don’t understand _____ he said
A. What; that; what B. What; what; what
C. That; that; what D. Why; that; which
key: A
47. Things were not _____ they seemed to be.
A. when B. why C. that D. what
key: D
48. That’s _____ I want to say.
A. all what B. what C. all which D. what that
key: B
49. That’s _____ .
A. where our differences lie B. our differences lie there
C. where do our differences lie D. that where our differences lie
key: A
50. That is _____ .
A. where lived he there B. where did he live
C. where he lived D. that where he lived
key: C
51. The questions is _____.
A. whether is it worth doing B. that if it is worth doing
C. whether it is worth doing D. if it is worth doing
key: C
52. Water will continue to be _____ it is today next in importance to oxygen.
A. how B. which C. what D. as
key: C
53. That's_____.
A. how did I become a teacher B. how I became a teacher
C. how a teacher I became D. that I became a teacher
key: B
54. They are just _____.
A. that what shall I have B. what shall I have
C. that I shall have what D. what I shall have
key: D
55. It looked ____.
A. as if it was going to rain B. that as if it was going to rain
C. as if was it going to rain D. as if that it was going to rain
key: A
56. That's_____.
A. how she did it B. that how did she do it.
C. how did she do it D. what she did it
key: A 注意选项D,多了一个词: it
57. That is _____ we decided to put the discussion off.
A. where B. which C. that D. why
key: D
58. That’s _____ I lived when I was ten years old.
A. where B. at which C. there where D. when
key: A
59. My suggestion is _____ we should send a few comrades to help them.
A. if B. that C. when that D. that where
key: B
60. The idea _____ all people are selfish is wrong.
A. what B. that C. why D. if
key: B
61. We heard the news _____ our team had won.
A. that B. what C. whether D. why
key: A
62. The fact _____ he hadn’t said anything surprised us all.
A. why B. if C. that D. whether
key: C
63.I have no idea _____ she will be back.
A. that B. where C. that when D. when
key: D
64. We must keep in mind the fact _____ China is still a developing country.
A. whether B. that C. why D. when
key: B
65. They have no idea at all _____.
A. where he has gone B. where did he go
C. where has he gone D. which place he has gone
key: A
高考英语语法: 省略介词的七种常见情形1
一:非谓语:(1)形式有三种:动词不定式,动名词,分词。
动词不定式相当于名词,形容词,副词,可做主语,宾语,宾补,表语,定语,状语(即谓语以外的所有句子成分);动名词相当于名词,可做主语,宾语,表语,定语;分词相当于形容词,副词,可做宾补,表语,定语,状语;
(2)语态:若逻辑主语是动作的发出者,则用主动;若逻辑主语是动作的承受者,则用被动;若逻辑主语既不是动作的发出者也不是承受者,则:动词不定式用独立结构
动名词用复合结构
分词用独立主格结构
举例:A)动词不定式作主语:To finish my homework is my job.
宾语:I want to have a wise brain.
宾补:I want you to attend the meeting.
表语:You job is to earn money.
定语:He is to go to college.
状语:I get up early in order to recite the poem.
独立结构:To tell you the turth,I am a student.
注意:1:有些宾语的不定式有自己的补语,则应用it做形式宾语,而将真正的宾语后置,如:I think it important to study English well.
2:不定式一般不做介词的宾语,除在极少数介词后才行(如but,except),此时动词不定式可带to也可不带to,如:He seldom comes except (to)see my daughter.
B)动名词做主语:Reading is my habbit.
宾语:The old need looking after.
表语:I am reading.
定语:He was looking the hanging picture.
复合结构:Alan's illness accounts for his coming late for school.
注意:1:一些特殊句式,如It is no good(no use,fun,a wast of time)+doing
There is no.....+doing
2:动名词复合结构的一般规则是:逻辑主语是有生命的名词,作主语时,须用名词的所有格形式或形容词性物主代词;作宾语时,可用普通格或人称代词宾格。
C):分词作宾补:I mind your somking.
表语:The news is encouraging./The glass is broken.
定语:This is a reading room./The book written by him is interesting.
状语:Seen from the top of the mountain,the city is beautiful.
二:虚拟语气:
A):在条件从句中:
1):表示与事实相反 条件从句的谓语形式 主句的谓语形式
表示现在情况 if+主语+did should/would/could/might+do
表示过去情况 if+主语+had done should/would/could/might+have done
表示将来情况 if+主语+were to do should/would/could/might+do
if+主语+should do
if+主语+did
2):在省略if的条件从句中,从句有were,should,had时,可省略if,而把它们置于主语之前,如:
If I had had time, I would have made an appointment with you.变成Had I have time,I would have an appointment with you.
3):介词without引导的短语可用来代替if引导的虚拟条件从句,如:If there were no water,fish couldn't live.
可由Without water,fish couldn't live.来代替。
4):错综时间的条件从句,主句和从句的谓语动词要依照设定的时间而定。如:If you had studied hard at that time,you would do it easily now.
B);在宾语从句中
1):在一些表示“坚持,命令,要求,建议”的词(如insist,command,order,require,request,desire,demand,advise,suggest,propose)后面接的宾语从句用should do,should可省略。
2):wish引导的宾语从句有三种情况:
1,现在:用过去式;
2,过去:用过去完成时;
3,将来:用(would/could)+do。
3):在would rather引导的宾语从句中
当从句表示现在或将来的时间时,谓语动词用一般过去式;表示过去的时间时,谓语动词要用过去完成时。
C):在主语从句中
在句型“It is strange/necessary/natural/important/right/pity/sorry+that......”中,that后面从句的谓语动词用:should do。注意:有些过去分词可以当形容词使用,在主语从句中要用虚拟语气,如It is ordered/commanded/required/advised/suggested that we/you /he/ she(should)+do .
D):在表语从句中
主句的主语常是表示说话人的命令,要求,建议,愿望等的名词(如order,command,requirement,demand,advise,suggestion,wish,desire),表语从句的谓语动词用(should)+do.如:Our suggestion is that you (should)be there on time.
E):在同位语从句中
同位语从句的先行词常是说话人愿望,建议,要求,命令等的名词。如:We put up with our suggestion that you (should) be there on time.
F):在as if从句中
1):在as if从句中,常用虚拟语气,即表示与现在事实相反,用过去式;与过去事实相反用过去完成式。
2):当不接虚拟语气时,表示可能或真实的情形。如:It looks as if it is going to rain.
3):虚拟语气中的几个特例
1,if only 意为:若是……那该多好啊;真希望……;只要,只要……就好了,如:If only I could fly.
2,It's(high)time that……that从句要用虚拟语气:谓语动词用过去式或should do 。如:It's high time that we should go.
3,一些短语,如:but for(要不是),without,otherwise(否则),in that case(如果那样的话),表示含蓄的条件,这是主句要用虚拟语气。如:Without your help,I couldn't finish it on time.
三:倒装句
A):完全倒装:谓语的全部放在主句之前。(此结构常只用于一般现在时和一般过去时)
1)用在there be结构中,此外,在此结构中可用来代替be的动词有exist,seem,happen,appear,hve,rise,stand等。如:There are many students in my classroom.
2):表示时间、地点和动作转移的副词如now,then,here,there,up,down,in,away,out等置于句首时,为使生动地描述情景而采用倒装语序,谓语动词常用动语come,go,be,lie,run,rush等。如:Now comes your turn.
注意:当代词作主语时,主谓语序不变。如:Here it is.
3):当句首为表示地点的介词词组时,也常引起全部倒装。如:From the valley came a frightening sound.
4):为平衡句子结构,或使上下文衔接紧密,表语置于句首时,倒装结构为:表语+连系动词+主语
1,“形容词+连系动词+主语”如:Present at the meeting were my sister.
2,“过去分词+连系动词+主语”如:Gone are the days when we were poor.
3,“介词短语+be+主语”如:Among the goods are flowers and toys.
B):部分倒装:只把系动词、助动词、情态动词放在主句之前。
1):在疑问句中,如:Can you speak English?
2):用于“never,hardly,seldom,scarely,rarely,barely,little,often,at no time(决不),by no means(绝不),under no circumstances(在任何一种情况下都不),in no case(绝不),in no way(决不)”等含有豆丁意义的副词或连词在句首的句型中。如:Little did he care about his own safety.
3):用于“no sooner....than....,hardly.....when.....,和not until....,not only....but alsol....,neither....nor”的句型中,主句部分用部分倒装。如:Not until the children fell asleep did the mother leave the room.
4):"only+状语"置于句首是要进行部分倒装,状语包括副词,介词短语和状语从句。如:Only then did he realise the importance of English.
5):用于“so/such....that"句型,so/such置于句首时,要部分倒装。如:So fast did he run that I couldn't catch up with him.
6):用于“形容词(或名词,动词)+as (though)"引导的让步状语从句中。如:
Try as you would, you might fail again.
Beautiful as she is,she isn't clever.
Child as he is ,he knows a lot.
7):用于省略if 的条件状语从句中,把助动词were,had,should提到主语前面。
高考英语语法:高中英语语法-主谓一致
高考英语语法:省略介词的七种常见情形
1. 介词on的省略
表示星期、日期等的时间的介词on有时可省略:
I’ll arrive (on) Friday. 我将星期五到。
See you (on) June 21st. 6月21日见吧。
2. 介词for的省略
(1) 表示一段时间或距离前的介词有时可省略:
I lived there (for) ten years. 我在那儿住了10年。
They walked (for) fifty miles. 他们走了50英里。
但在否定句中或用于句首时,介词for通常不能省略:
For ten years he lived here. 他在这里住过10年。
We have not heard from him for a long time. 我们很久没收到他的来信了。
另外,若所修饰的动词不是在整个时间范围内都自始自终延续,则for也不省略:
I taught her for three years. 我教过她三年。(其中的for不能省略)
(2) 某些结构中表示原因的介词for有时可以省略:
Pardon me (for) interrupting you. 请原谅我打断你的话。
We quite envy you (for) your success. 我们十分羡慕你的成功。
Please forgive me (for) my fault. 请原谅我的过错。
3. 介词at的省略
what time前的介词at通常可以省略:
What time did he leave here? 他是什么时候离开这儿的?
另外,在“about [around]+时间名词”前的介词at也通常省略:
He arrived (at) about ten o’clock. 他大约(在)10点钟到的。
at home 这一短语中的介词at在美国英语中通常省略:
Let’s stay (at) home this evening. 今晚我们就呆在家里吧。
4. 介词of的省略
all of, both of, half of 用于带限定词(如my, the, these等)的名词前时,其中的介词of通常可以省略:
All (of) the students have passed the exam. 所有的学生都考及格了。
Both (of) my parents are interested in history. 我的父母都对历史感兴趣。
Half (of) the milk had been drunk. 有一半牛奶已被喝了。
注若用于人称代词前,则其中的of不可省略:
All (Both, Half) of us wanted to leave. 我们大家(俩,有一半人)都想走。
5. 介词from的省略
在 prevent [stop]…from doing sth(阻止…发生),save…(from) doing sth(免去…做某事)等结构中的介词from通常可以省略:
The heavy rain prevented him (from) coming. 大雨使他不能来。
If I can stop them (from) going there, I’ll do it. 要是我能够阻止他们去那里,我会这样做的。
If you do it tonight, it will save you (from) having to get up early. 你如果今晚做这事,明天早上你就不必早起了。
注在被动语态中from通常不宜省略。另外,在表示类似含义的prohibit…from doing sth 中的from习惯上不省略,而在与此同义的keep…from doing sth中,from则绝不可省略,否则含义不同:
He kept me from working. 他不让我工作。
He kept me working. 他要我不停地工作。
高考英语语法:高中英语语法-实用英语五十句
《高中英语语法-主谓一致》由留学liuxue86.com我整理。本内容整理时间为05月12日,如有任何问题请联系我们。
主谓一致
语法复习二、主谓一致
在英语句子里,谓语受主语支配,其动词必须和主语在人称和数上保持一致,这就叫主谓一致。寻其规律,大致可归纳为三个原则,即语法一致、逻辑意义一致和就近一致原则。
(一)语法一致原则:语法上一致就是谓语动词和主语在单、复数形式上保持一致。
1、以单数名词或代词、动词不定式短语、动名词短语或从句作主语时,谓语动词一般用单数形式;主语为复数时,谓语动词用复数形式。如:His father is working on the farm. / To study English well is not easy. / What he said is very important for us all. / The children were in the classroom two hours ago. / Reading in the sun is bad for your eyes.
注意:由what引导的主语从句,后面的谓语动词多数情况用单数形式,但若表语是复数或what从句是一个带有复数意义的并列结构时,主句的谓语动词用复数形式。如:What I bought were three English books. / What I say and do is (are) helpful to you.
2、由连接词and或both ? and连接起来的合成主语后面,要用复数形式的谓语动词。如:Lucy and Lily are twins. / She and I are classmates. / The boy and the girl were surprised when they heard the news. / Both she and he are Young Pioneers.
注意:① 若and所连接的两个词是指同一个人或物时,它后面的谓语动词就应用单数形式。如:The writer and artist has come.; / ② 由and连接的并列单数主语前如果分别有no, each, every more than a (an) , many a (an)修饰时,其谓语动词要用单数形式。如:Every student and every teacher was in the room.. / No boy and no girl likes it.
3、主语为单数名词或代词,尽管后面跟有with, together with, except, but, like, as well as, rather than, more than, no less than, besides, including等引起的短语,谓语动词仍用单数形式;若主语为复数,谓语用复数形式。如:Mr Green, together with his wife and children, has come to China. / Nobody but Jim and Mike was on the playground. / She, like you and Tom, is very tall.
4、either, neither, each, every 或no +单数名词和由some, any, no, every构成的复合不定代词,都作单数看待。如:Each of us has a new book. / Everything around us is matter.
注意:① 在口语中当either或neither后跟有"of+复数名词(或代词)"作主语时,其谓语动词也可用复数。如:Neither of the texts is (are) interesting. ② 若none of后面的名词是不可数名词,它的谓语动词就要用单数;若它后面的名词是复数,它的谓语动词用单数或复数都可以。如:None of us has (have) been to America.
5、在定语从句时,关系代词that, who, which等作主语时,其谓语动词的数应与句中先行词的数一致。如:He is one of my friends who are working hard. / He is the only one of my friends who is working hard.
6、如果集体名词指的是整个集体,它的谓语动词用单数;如果它指集体的成员,其谓语动词就用复数形式。这些词有family, class, crowd, committee, population, audience等。如:Class Four is on the third floor. / Class Four are unable to agree upon a monitor.
注意:people, police, cattle等名词一般都用作复数。如:The police are looking for the lost child.
7、由"a lot of, lots of, plenty of, the rest of, the majority of + 名词"构成的短语以及由"分数或百分数+名词"构成的短语作主语,其谓语动词的数要根据短语中后面名词的数而定。如:There are a lot of people in the classroom. / The rest of the lecture is wonderful. / 50% of the students in our class are girls.
注意: a number of"许多",作定语修饰复数名词,谓语用复数;the number of"?的数量",主语是number,谓语用单数。
8、在倒装句中,谓语动词的数应与其后的主语一致。如:There comes the bus./ On the wall are many pictures. / Such is the result. / Such are the facts.
(二)逻辑意义一致原则:逻辑意义一致就是谓语动词的数必须和主语的意义一致(因有时主语形式为单数,但意义为复数;有时形式为复数,但意义为单数)。
1、what, who, which, any, more, all等代词可以是单数,也可是复数,主要靠意思来决定。如:Which is your bag? / Which are your bags? / All is going well. / All have gone to Beijing.
2、表示"时间、重量、长度、价值"等的名词的复数作主语时,谓语动词通常用单数形式, 这是由于作主语的名词在概念上是一个整体,如:Thirty minutes is enough for the work.
3、若英语是书名、片名、格言、剧名、报名、国名等的复数形式,其谓语动词通常用单数形式。如: "The Arabian Nights"is an interesting story-book.
4、表数量的短语"one and a half"后接复数名词作主语时,其谓语动词可用单数形式(也可用复数。如:One and a half apples is (are) left on the table.
5、算式中表示数目(字)的主语通常作单数看待,其谓语动词采用单数形式。如:Twelve plus eight is twenty. / Fifty-six divided by eight is seven.
6、一些学科名词是以 -ics 结尾,如:mathematics, politics, physics 以及news, works等,都属于形式上是复数的名词,实际意义为单数名词,它们作主语时,其谓语动词要用单数形式。如:The paper works was built in 1990. / I think physics isn't easy to study.
7、trousers, glasses, clothes, shoes, 等词作主语时,谓语用复数,但如果这些名词前有a (the) pair of等量词修饰时,谓语动词用单数。如:My glasses are broken. / The pair of shoes under the bed is his.
8、"定冠词the + 形容词或分词",表示某一类人时,动词用复数。
(三)就近一致原则:在英语句子中,有时谓语动词的人称和数与最近的主语保持一致。
1、当两个主语由either ? or, neither ? nor, whether ? or ?, not only ? but also连接时,谓语动词和邻近的主语一致。如:Either the teacher or the students are our friends. / Neither they nor he is wholly right. / Is neither he nor they wholly right?
2、there be句型be动词单复数取决于其后的主语。如果其后是由and连接的两个主语,则应与靠近的那个主语保持一致。如:There are two chairs and a desk in the room..
注意:Here引导的句子用法同上。
练习:主谓一致
1.I, who____ your friend, will try my best to help you with your English.
A.am B.is C.are D.be
2. The rich ____ not always happy.
A.are B.is C.has D.have
3. Neither Tom nor Jack and I ____ his students.
A.are B.am C.is D.was
4. Mary as well as her sisters ____ Chinese in China.
A. are studying B. have studied C. studies D. study
5. Neither my father nor I ____ at home.
A.am B.is C.are D.be
6. Not only my brother but also I ____ good at painting. Both of us ____ good painters.,
A.are;are B.am;am C.ani;are D.is;is
7. Every' boy and every girl ____ to attend the evening party.
A.wish B.wishes C.is like D.like
8. Over 80 percent of the population of China ____ peasants.
A.was B.is C. would be D.are
9. The population of China ____ larger than that of .any other country in the world.
A.is B.are C.has D.have
10. Every means ____ tried but without any result.
A. have been B.is to be C.are to be D. has been
11. Alice, together with two boys,____ for having broken the rule.
A. was punished B. punished C. were punished D. being punished
12. The League secretary and the monitor____ asked to attend the .meeting this afternoon.
A.is B.was C.are D.is being
13. The great writer and professor____.
A. is an old man B. are both old men
C. is an old man and a young man D. were two Chinese
14. There ____ a pen, two pencils and three books on the desk.
A.are B.is C.has D.have
15. A large number of students in our class____ girls.
A. are B. was C. is D. be
16. The number of deer, mountain lions and wild roses ____ much if people leave things as they are.
A. doesn' t change B.don't change C.change D.changed
17. The Arabian Nights ____ well known to the English.
A. is B. are C. was D. were
18. Chairman Mao' s works ____ published.
A. has been B.have been C.was D.is
19. A chemical works____ built there.
A. is to being B.have been C. were to D.has been
20. The Olympic Games ____ held every ____ years.
A.is;four B.are;four C.is;five D.are;five
21 .The United States of America one of the most developed countries in the world.
A.is B.are C.was D.were
22.He is the only one of die students who ____ elected.
A. are B.have C.has D.is
23.Theis is one of the most interesting questions that ____ asked.
A.have B.has C. have been D.has been
24.Many a man ____ come to help us.
A.have B.has C.is D.are
25."All____ present and all____ going on well," our monitor said.
A.is;is B.are;are C.are;is D.is;are
26. The police ____ the murderer everywhere when he suddenly appeared in a theatre.
A. is searching for B. were searching for
C. are searching for D. were searching
27.Your trousers____ dirty.You must have____ washed.
A.is;il B.are;it C.are;them D.is;them
28.This pair of trouseis ____ too long for him.
A.is B.be C.are D.were
29. One and a half bananas ____ left on the table.
A.is B.are C.has D.have
30. Eight times eight ____ sixty - four.
A.is B.are C.get D.equal
31 .Ten minutes____ an hour when one is waiting for a phone call.
A.seems B.seem C.seemed D.seemes
32.____of the money____ nm out.
A. Three-fifth; has B. Three-fifth; has been
C. Three-fifths; has D. Three-fifths; have
33. The whole class ____ the teacher attentively.
A. are listening to B. is listening to
C.are listening D. is listening
34.1 have finished a large part of the book, the rest of which___ more difficult.
A.is B.are C.was D.were
35. Between the two rows of trees ____ the teaching building.
A.stand B.stands C. standing D.are
36. Large quantities of water ____ for irrigation.
A. is needed B. has -needed C. are needed D. need
37. That they were wrong in these matters ____ now clear to us all.
A. is B.was C.are D.all
38.What we need____ good textbooks.
A.is B.are C.have D.has
39. What you said just now____ the matter we are discussing.
A.have something to at B. has something to do with
C.had something to do with D.has been something to do with
40. More than one member ____ against the plan.
A. is B.are C.has D.have
41. When and where to build the new factory ____ yet.
A. has not decided B. is not decided
C. are not decided D. have not decided
42. Half of the fruit ____ bad.
A. are B. has C. is D. have
43. ____ either of your parents come to see you recently?
A. Have B. Had C. Has D. Is
44. Mathematics ____ the language of science.
A. are B. are going to be C. is D. is to be
45. My family ____ small.
A. is B. were C. are D. makes
46. The following ____ some other examples.
A. are B. is C. was D. were
47. They both have some friends; but his ____ more active.
A. is B. will be C. was D. are
48. Both rice and wheat ____ grown in that country.
A. is B. are C. was D. has
49. Early to bed and early to rise ____ a good habit.
A. are B. is C. were D. was
50. To play basketball and to go swimming ____ useful for character-training.
A. was B. is C. are D. were
51. Either he or I ____ to attend the mass meeting this evening.
A. is B. am C. are D. be
52. ____ either he or I to attend the mass meeting this evening.
A. is B. am C. are D. be
53. An iron and steel works, with some satellite factories, ____ to be built here.
A. are B. were C. is D. will
54. She as well as her brother ____ a League member.
A. are B. were C. will D. is
55. His family ____ a big one. Now the family ____ watching TV.
A. is, are B. are, is C. is, is D. are, are
56. It is I who ____ going to attend the meeting tomorrow.
A. is B. am C. are D. be
57. More than 60% of the students ____ the countryside.
A. is B. are C. is from D. are from
58. Many a man ____ the novel.
A. has read B. have read C. is read D. are read
59. Tom is the only one of the students who ____ going to swim this afternoon.
A. is B. was C. are D. were
60. Here ____ a pen, a few pencils and some paper for you.
A. are B. is C. was D. were 《高中英语语法-主谓一致》由留学liuxue86.com我整理
高考英语语法填空必背知识
《高中英语语法-实用英语五十句》由英语我整理,更多请访问:。本内容整理时间为05月12日,如有任何问题请联系我们。
实用英语五十句
支持别人的十句话
1. I will support you.
我会支持你的。
2. I"ll back you up.
我会挺你的。
3. I"m on your side.
我站在你这边。
4. You can count on me.
你可以依靠我。
5. You can rely on me.
你可以依赖我。
6. You can trust in me.
你可以信赖我。
7. I"ll be available if you need me.
你需要帮助时,我就有空。
8. I"ll be there if you need a hand.
你需要帮助时,我就会出现。
9. I"m a phone call away.
我随call随到。
10. I"m with you all the way.
我一路上陪着你。
命令别人的十句话
1. Do as I tell you.
照我的话做。
2. Don"t question what I say.
别质疑我的话。
3. Do what you are told.
叫你怎么做,你就怎么做。
4. Do as I say, and you"ll be just fine.
照我的话做就没错了。
5. Shut your mouth and do it.
闭嘴照做。
6. Just do it.
做就是了。
7. You"d better take me seriously.
你最好把我的话当真。
8. Don"t ever disobey me.
别想违背我。
9. My way or the high way.
照我的方式做,不然就滚蛋。
10. Listen, I"m the one who calls the shots here.
听好,这里由我做主。
追求异性的十句话
1. You"ve given me a reason to live.
你给了我活下去的理由。
2. I"m drawn to you.
我被你吸引。
3. I"m so happy I met you.
真高兴能认识你。
4. You"re a knockout.
你美(帅)呆了。
5. I"m mad about you.
我为你疯狂。
6. I fell in love with you the moment I saw you.
见到你的那一瞬间,我就爱上你了。
7. You fill my life with joy.
你使我的生命充满喜悦。
8. I want to be with you for the rest of my life.
我要和你共度余生。
9. I didn"t stop thinking about you all day.
我整天都在想你。
10. You complete me.
你使我的生命更完整。
「与老外搭讪」的十句话
1. Where are you from?
你从哪里来?
2. How long have you been in Taiwan?
你来台湾多久了?
3. Do you speak Chinese?
你会说中文吗?
4. Wow, where did you pick up your Chinese? You speak Chinese so well!
哇,你在哪里学的中文?你中文讲得好棒喔!
5. Why did you come to Taiwan? Did you come here to study Chinese or just
visit?
你为什么来台湾?你来台湾学中文还是只是观光?
6. What do you do in Taiwan?
你在台湾从事什么工作?
7. Do you like Chinese food?
你喜欢中国食物吗?
8. Are you interested in doing a language exchange with me?
你有兴趣和我做个语言交换吗?
9. What do you like about Taiwan?
你喜欢台湾哪些东西?
10. Where have you been in Taiwan?
你去过台湾哪些地方?
形容「身材」的十句话
1. She is thin / fat.
她瘦瘦的。 / 她胖胖的。
2. He"s big / small.
他个头满大的。/ 他个头小小的。
3. She"s slim.
她很苗条。
4. She"s really skinny.
她瘦得跟皮包骨一样。
5. She is chubby.
她胖嘟嘟的。
6. He has a beer belly.
他有啤酒肚。
7. He"s got a spare tire. / He"s got love handles.
他有游泳圈。(他腰部都是赘肉。)
8. He"s very muscular.
他肌肉很发达。
9. She has an hourglass figure. / She"s got a curvy figure.
她的身材玲珑有致。/ 她曲线玲珑。
10. She"s pretty stacked.
她身材身材婀娜多姿 《高中英语语法-实用英语五十句》由英语我整理,更多请访问: 英语高考的时候,不管是单词、 短语 、句型还是语法,都会被考察到,所以考生们一定要全面复习好这些知识。下面是我整理分享的高考英语语法填空必背知识,欢迎阅读与借鉴,希望对你们有帮助!
高考英语语法填空必背知识
一、部分过去式和过去分词不规则变化的动词
1. broadcast (broadcast, broadcast) 广播
2. flee (fled, fled) 逃跑
3. forbid (forbade, forbidden) 禁止
4. forgive (forgave, forgiven) 原谅
5. freeze (froze, frozen) 结冰
6. hang (作“绞死”讲,是规则的;作“悬挂”讲,其过去式过去分词都是hung)
7. lie (作“说谎”讲时,是规则的;作“位于”讲时,其过去式是lay,过去分词是lain)
8. seek (sought, sought) 寻求
9. shake (shook, shaken) 发抖
10. sing (sang, sung) 唱歌
11. sink (sank, sunk/sunken) 下沉
12. spread (spread, spread) 传播
13. swim (swam, swum) 游泳
14. tear (tore, torn) 撕碎
15. weave (wove, woven) 编织
二、以下动词加-ed或-ing要双写最后一个字母
双写规则口诀:重读闭音节有特点,词尾是两“辅”夹一“元”。
若把-ing,-er(-est),-ed添,辅音字母要双写全。
注:两“辅”夹一“元”:指单词最后三个字母是“辅音字母+元音字母+辅音字母”(最后一个字母如是w,x,y除外),其中元音字母所发的音是该单词的重音。即“以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节词”。
1. admit (admitted, admitting) 承认
2. permit (permitted, permitting)允许
3. regret (regretted, regretting) 后悔
4. forget (forgotten, forgetting ) 忘记 unforgettable
5. control (controlled, controlling) 控制
6. occur (occurred, occurring) 出现
7. prefer (preferred, preferring) 宁愿
8. refer (referred, referring) 提到
9. equip (equipped, equipping) 装备
注意:quarrel, signal, travel中的l可双写(英国英语)也可不双写(美国英语) 另外注意:destroy (destroyed) employ (employed)
shyer; shyest
三、容易拼写错的数字
1. eighth第八 2. ninth第九 3. forty四十 4. twelfth第十二
5. twentieth第二十
四、注意形容词变名词时的拼写变化
1. long—length 长度— lengthen加长
2. wide—width 宽度—widen
3. high—height 高度—heighten
4. strong—strength力量 —strengthen
5.deep—depth—deepen
6. short—shortness—shorten
7.broad—broadness—broaden
8.large—largeness—enlarge
五、以-ic结尾的动词,应先把-ic变为-ick,再加ing或ed
1. picnic (picnicked, picnicking) 野餐
2.panic (panicked, panicked) a./ v.惊慌,恐慌,惶恐不安
六、个别名词的'复数拼写
1. German (Germans) 德国人
2. gulf (gulfs) 海湾
3. handkerchief (handkerchiefs) 手帕
4. hero (英雄),potato (土豆),tomato (西红柿) 等有生命的以-o结尾的名词变复数时要加-es。
5. roof (roofs) 房顶
6. stomach 胃 (其复数是stomachs而不是加es)
七、常用复数形式
1. headphones (耳机), trousers (裤子),sunglasses (太阳镜), scissors (剪刀), compasses (圆规)
2. noodles, vegetables, snacks小吃, 快餐,
3. make friends with 与...交朋友,in high/low spirits (情绪高涨/低落), have sports (进行体育活动)。
4. congratulations (祝贺)。
5. celebrations (庆祝),
八、注意动词变名词时的拼写变化
1. succeed—success成功
2. pronounce—pronunciation 发音
3. explain—explanation解释
4. decide—decision 决定
5. enter—entrance进入
6. permit—permission 允许
7. refuse—refusal 拒绝
8. consider—consideration 考虑
9. discover—discovery 发现
10. bury—burial 埋葬
11. conclude—conclusion 得出结论
12. arrive—arrival 到达
13. weigh—weight 重量
14.press--pressure压力
九、注意去不去e
possible—possibly 可能的 argue—argument judge—judgment
value—valuable courage—courageous
高考英语语法填空必背知识相关 文章 :
★ 高考英语语法填空进行时态知识点与必记的单词
★ 高考英语语法填空考点总结
★ 英语高考语法填空《英语语法手册》知识点
★ 高考英语语法填空一般时态知识点与训练题
★ 高考英语语法填空动词知识点与语法填空题与答案
★ 高考英语语法填空副词知识点与练习题
★ 高考英语语法填空解题策略
★ 英语高考语法填空规律总结与练习题
★ 高考英语语法填空技巧整理
★ 高考英语语法填空比较级知识点与强化训练题